Insulin hormone deficiency is a disease known to mankind since ancient times, but despite this and the rapid development of medical technologies, acquiring new knowledge about the disease is extremely difficult to identify it in the early stages. Many patients are not even aware of the presence of diabetes mellitus, attributing the symptoms to hormonal changes in the body and other diseases. Diabetes mellitus negatively affects health and metabolic processes, so it is extremely important to identify it as early as possible and start treatment on time.
What is diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrinological disease that develops as a result of insulin deficiency. A hormone synthesized by the pancreas is involved in the breakdown of sugar and the transport of glucose through the blood to the tissues of the organs to provide the body with extra energy. In the case of insulin deficiency, the sugar level rises significantly, which negatively affects the whole body.
Causes of disease development
The disease most often occurs in the presence of the following causes or conditions:
- Hereditary predisposition, especially if the father suffers from diabetes, the likelihood of developing the disease in children is much higher than if the disease is observed in the mother.
- Improper diet - abuse of foods high in calories, glucose and carbohydrates.
- The presence of excess weight, and with the second and subsequent degree of obesity, the likelihood of developing diabetes mellitus increases by 80%.
- Lack of physical activity, low human activity.
- Frequent experiences of stressful situations or prolonged depression. A severe stroke or a nervous breakdown can also provoke an illness.
- Long-term use of drugs of a certain group, for example, hormonal, diuretic or choleretic.
- Presence of a viral infection in the body (chickenpox, flu, rubella).
Symptoms of the disease
Warning signals that are evidence of the presence of the disease include:
- The constant feeling of thirst, which does not disappear even after heavy drinking.
- Frequent urination, especially at night. This causes some worries and annoyances, violates the established way of life.
- Drops of urine remain on the fabric, which when dried, resemble traces of dried starch (white and dense spots).
- The person complains of fatigue and drowsiness.
- Visibility is significantly reduced, all objects look blurry.
- It is often accompanied by a tingling sensation and numbness, especially in the palms and soles of the feet.
- Slow and very poor wound healing, even the smallest and most insignificant.
- The patient is concerned about itching, which is particularly strong in the groin area.
- Sudden weight loss for no apparent reason.
- Strong hunger that is hard to satisfy.
It is important to remember that many of the symptoms already appear when there is a lack of insulin in the body and irreversible processes of cessation of hormone production by the pancreas have begun. It is extremely difficult to diagnose the disease in the initial stage, so 80% of patients are not aware of the presence of the disease.
Types of diabetes
There are 2 types of diabetes mellitus, which have characteristic differences despite some similarities.
- Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes is a disease characterized by the death of pancreatic beta cells, the main role of which is insulin production. As a result of this process, a hormone deficiency appears, which provokes diabetes. Causes of the development of the disease include a violation of the immune system, the presence of a viral infection in the human body. As a rule, this type of disease affects children and adolescents. The only treatment option for the disease are regular insulin injections for the rest of life.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a disease that affects people over the age of thirty and develops as a result of lack of perception by the body, tissue cells and organs of insulin produced by the pancreas. Due to the improper reaction of the body to the hormone, glucose accumulates in the blood and provokes the flow of negative processes in the body. In case of premature treatment, insulin production stops completely, as an increased level of blood glucose negatively affects beta cells and contributes to their destruction.
Diagnosis of diabetes
To diagnose the disease, you should contact the clinic to see an endocrinologist who specializes in this disease. The following procedures and examinations are performed for examination:
- Fasting blood test for blood sugar level. In some cases, when the patient is at risk for disease, a stress test is performed to determine glucose tolerance.
- Perform a urine test for sugar content and determine its level. A urine test for the presence of acetone may also be performed.
- It is also important to perform an analysis for the installation of glycated hemoglobin, which will help determine the average blood glucose level over the last three months.
- It is important to remember that diabetes is a chronic disease that cannot be cured, so regular maintenance therapy is required to maintain a normal condition.

Treatment of the disease
The main treatment for type 1 (insulin dependent) diabetes is regular insulin injections. Thanks to modern medical instruments, injections have become much easier; insulin pumps and pens are used for this. The dose of insulin is determined individually for each patient and it is not recommended to change it yourself. The amount of insulin depends on the blood sugar level, the presence of other concomitant diseases (for example, obesity), the patient's lifestyle.
In case of incomplete pancreatic insufficiency, the doctor may prescribe medications that can stimulate hormone production in the human body. To eliminate insulin resistance in the body, other groups of drugs can be used that eliminate insulin resistance and help maintain human health. An important factor is the observance of a special diet, in which foods are selected with a minimum content of sugar, carbohydrates, as well as stimulation of the pancreas.
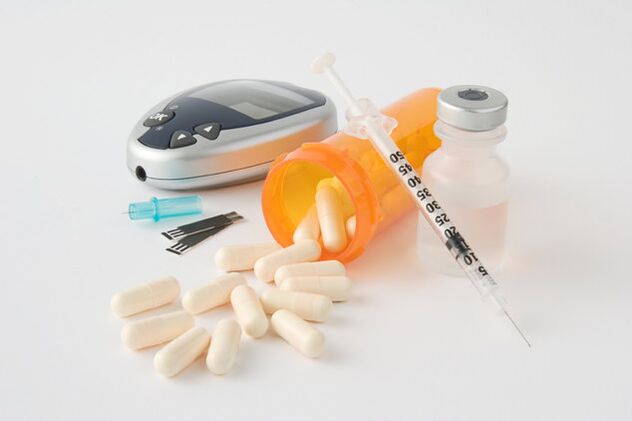
Disease prevention
To avoid the development of the disease, it is important to follow the recommendations of the endocrinologist, who will help maintain health and not fall into the risk group. Preventive methods include:
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is especially recommended for those at risk. People over the age of forty should have this study done regularly, at least twice a year.
- Changing eating habits, switching to a balanced diet with a predominance of healthy foods - fruits, vegetables, fish, lean meats with low glucose. In addition, it is recommended to follow a diet and divide the food intake into three equal meals and some snacks.
- Perform simple daily physical exercises, which will help normalize weight and reduce the likelihood of developing diabetes.
- Weight normalization, which will help reduce the likelihood of developing the disease.